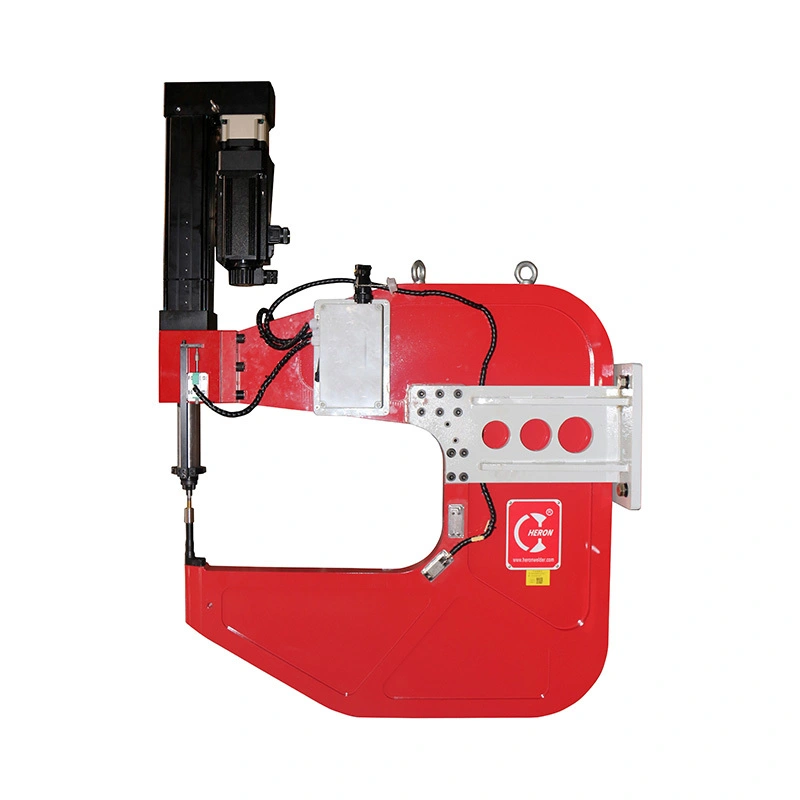
When manufacturers look for fast, clean, and high-strength sheet metal joining methods without heat, sparks, or filler materials, the clinching machine stands out as one of the most efficient solutions. In automotive production, white goods manufacturing, HVAC ducting, metal cabinets, enclosures, and general sheet fabrication, clinching has become a proven alternative to welding, riveting, and adhesive bonding — especially when sustainability, cost efficiency, and cycle time matter. For manufacturing engineers, OEMs, and automation integrators, understanding how clinching works and when to apply it is critical to designing reliable production systems.
What Is a Clinching Machine?
A clinching machine is a mechanical sheet-metal joining system that joins two or more metal sheets by deforming and interlocking the material layers using a punch and die. No heat input, no consumables, and no additional fasteners are required.
Instead of melting material (like resistance welding) or inserting rivets, the clinching process forms a local cold-formed interlock. This makes the joint robust, repeatable, and ideal for coated, galvanized, or dissimilar metal combinations where traditional welding may face quality challenges.
How Does a Clinching Machine Work? (Principle of Operation)
Clinching machines use controlled force and precision tooling to produce a consistent joint. The process typically follows four stages:
-
Clamping – The sheets are positioned between punch and die while a holder clamps them securely.
-
Punching/Deformation – The punch applies force, pushing material into the die cavity.
-
Interlocking Formation – The material flows plastically, creating a button-shaped mechanical interlock.
-
Release – The punch retracts, resulting in a permanent joint without damaging coatings or structural integrity.
Heron Welder’s advanced clinching technology ensures tight dimensional tolerance, high repeatability, and stable joint consistency, supporting both manual stations and fully automated production lines.
Applications Across Industries
Clinching machines are widely adopted in:
Automotive & Mobility
-
BIW components
-
Trunk covers, seat structures
-
Chassis brackets and reinforcement parts
-
EV battery enclosures
White Goods & Appliances
-
Washing machines
-
Refrigerators
-
Ovens and microwave housings
HVAC & Sheet Metal Fabrication
-
Air ducts
-
Ventilation units
-
Steel cabinets and control panels
Electronics & Industrial Equipment
-
Metal furniture
-
Electrical enclosures
-
Machinery covers and frames
Whenever thin-sheet metal joining (0.3–4mm combined thickness) is required with high structural reliability and productivity, clinching machines deliver an excellent balance of performance and cost.
Clinching vs Welding vs Riveting – Which Is Better?
Clinching machines solve many manufacturing pain points associated with traditional joining methods. Here’s how they compare:
Clinching vs Resistance Welding
Advantages of Clinching:
-
No heat → No thermal distortion
-
No sparks → Safer and cleaner working environment
-
Preserves zinc-coating and surface treatment
-
Excellent for dissimilar materials (steel + aluminum, coated sheets)
-
Lower energy consumption and maintenance
When Welding Is Preferred:
-
Very thick materials
-
Ultra-high structural load applications
Clinching vs Riveting
Advantages of Clinching:
-
No consumables → Reduced cost and logistics
-
Faster cycle time
-
No hole preparation required
-
Reduces structural weakening from drilled holes
When Riveting May Still Be Used:
-
Extremely high vibration environments
-
Non-deformable materials
Clinching vs Adhesive Bonding
Advantages of Clinching:
-
Instant joint — no curing time
-
High mechanical strength
-
More reliable under temperature variation
Types of Clinching Machines
Depending on production scale and integration needs, manufacturers can choose:
Manual Clinching Machines
Ideal for small batches, repair work, and flexible manufacturing environments.
Pneumatic / Hydraulic Clinching Systems
Suitable for medium to high-volume production with consistent joining quality.
Servo-Driven and MFDC Integrated Clinching Solutions
Provide enhanced control, stable force delivery, and compatibility with automated systems.
Robotic / Automated Clinching Cells
Designed for high-throughput automated manufacturing lines, with options for inline quality monitoring and data acquisition.
Heron Welder provides custom-engineered clinching stations, robotic solutions, and turnkey automation lines, tailored to customer production requirements.
Key Benefits of Using a Clinching Machine
-
Cost Efficiency – No consumables, reduced energy usage, minimal maintenance.
-
Environmentally Friendly – No emissions, smoke, or welding fumes.
-
Strong and Reliable Joints – Excellent fatigue resistance and mechanical strength.
-
High Productivity – Fast cycle times suitable for mass production.
-
Flexible Material Compatibility – Suitable for coated, painted, or dissimilar metals.
-
Automation Ready – Easy integration into Industry 4.0 production environments.
Best Practices for Selecting and Using a Clinching Machine
To ensure optimal performance, engineering teams should consider:
-
Material type and thickness combinations
-
Required joint strength and durability
-
Production volume and takt time
-
Accessibility of joint area
-
Automation and integration requirements
-
Quality monitoring needs
A reliable technology partner like Heron Welder helps evaluate these parameters, perform feasibility testing, and deliver a complete turnkey clinching solution optimized for performance, cost, and longevity.
Why Choose Heron Welder as Your Clinching Solution Partner?
With decades of expertise in resistance welding, clinching technology, mechanical fastening, and automated joining systems, Heron Welder supports global OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, and industrial manufacturers with:
-
Advanced clinching machines and tooling
-
Customized engineering solutions
-
Automated production lines
-
Stable quality, precision control, and long service life
-
Expert technical support and training
Heron is committed to delivering efficient, reliable, and future-ready metal-joining technologies that help factories achieve higher productivity and better profitability.
FAQs About Clinching Machines
1. What thickness can a clinching machine handle?
Typically, clinching is ideal for thin sheet metals between 0.3mm and 4mm combined thickness, depending on material strength and tooling.
2. Can clinching replace spot welding?
Yes, in many cases clinching offers equal or better performance, especially for coated metals, aluminum, and dissimilar metals, while reducing energy consumption and maintenance.
3. Is clinching suitable for automated production lines?
Absolutely. Clinching machines can be integrated with robots, transfer systems, and smart manufacturing cells for high-volume automated production.
4. Does clinching damage surface coating?
No. Clinching preserves coatings such as galvanization, paint, and plating, minimizing post-processing.
5. What industries benefit most from clinching machines?
Automotive, household appliances, HVAC, sheet metal fabrication, industrial equipment manufacturing, and electronics industries benefit significantly.
Ready to Upgrade Your Metal Joining Process?
If you’re evaluating clinching technology or looking to enhance your welding and joining capabilities, Heron Welder provides proven equipment, industry expertise, and fully customized automation solutions to match your production goals.
Contact Heron Welder today to discuss your application, request a quote, or schedule a technical consultation.