Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Forecast, Regional Insights, and Competitive Landscape (2023-2029)
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Overview
Maximize Market Research is a Business Consultancy Firm that has published a detailed analysis of the “Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market”. The report includes key business insights, demand analysis, pricing analysis, and competitive landscape. The analysis in the report provides an in-depth aspect at the current status of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market, with forecasts outspreading to the year.
Gain Valuable Insights – Request Your Complimentary Sample Now @ https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/71525/
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Scope and Methodology:
The market research report for Plastic for Consumer Electronics offers detailed insights into the key factors shaping industry growth, along with the challenges that may arise in the future. It equips stakeholders with a clear understanding of investment prospects, available product portfolios, and the competitive landscape within the Plastic for Consumer Electronics sector. The study also explores both quantitative and qualitative dimensions of the industry. As part of the MMR analysis, regional markets within the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market are examined extensively.
This report presents a comprehensive overview of all major and several minor market elements. The findings are based on data collected from both primary and secondary sources, including expert opinions, industry specialists, official websites, scientific journals, and company annual reports.
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Segmentation
by Product
•Polycarbonate (PC),
• Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
• Styrene-acrylonitrile resin (SAN)
• Acrylonitrile styrene acrylester (ASA)
• Polystyrene (PS)
• Poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA)
• Others
Feel free to request a complimentary sample copy or view a summary of the report @ https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/71525/
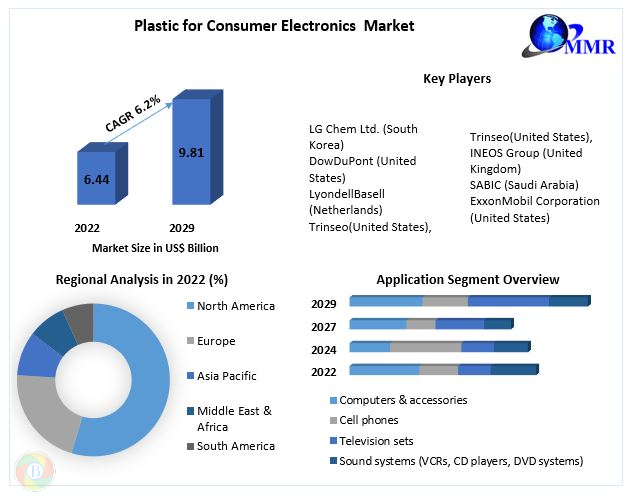
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Regional Insights
The market size, growth rate, import and export by region, and other relevant variables are all thoroughly analysed in this research. Understanding the Plastic for Consumer Electronics market conditions in different countries is feasible because to the researchs geographic examination. Africa, Latin America, the Middle East, Asia Pacific, and Europe put together make up the Plastic for Consumer Electronics market.
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Key Players
• Atotech (Germany)
• LG Chem Ltd. (South Korea)
• DowDuPont (United States)
• LyondellBasell (Netherlands)
• Trinseo(United States),
• INEOS Group (United Kingdom)
• SABIC (Saudi Arabia)
• ExxonMobil Corporation (United States)
Key questions answered in the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market are:
What is Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What is the growth rate of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Which are the factors expected to drive the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market growth?
What are the different segments of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What growth strategies are the players considering to increase their presence in Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What are the upcoming industry applications and trends for the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What are the recent industry trends that can be implemented to generate additional revenue streams for the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Who are the leading companies and what are their portfolios in Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What segments are covered in the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Explore More Market Reports:
Aluminum Foil Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-aluminum-foil-market/23912/
DevOps Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-devops-market/31505/
About Maximize Market Research:
Maximize Market Research is a multifaceted market research and consulting company with professionals from several industries. Some of the industries we cover include medical devices, pharmaceutical manufacturers, science and engineering, electronic components, industrial equipment, technology and communication, cars and automobiles, chemical products and substances, general merchandise, beverages, personal care, and automated systems. To mention a few, we provide market-verified industry estimations, technical trend analysis, crucial market research, strategic advice, competition analysis, production and demand analysis, and client impact studies.
Contact Maximize Market Research:
2nd Floor, Navale IT Park, Phase 3
Pune Banglore Highway, Narhe,
Pune, Maharashtra 411041, India
sales@maximizemarketresearch.com
+91 96071 95908, +91 9607365656
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Overview
Maximize Market Research is a Business Consultancy Firm that has published a detailed analysis of the “Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market”. The report includes key business insights, demand analysis, pricing analysis, and competitive landscape. The analysis in the report provides an in-depth aspect at the current status of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market, with forecasts outspreading to the year.
Gain Valuable Insights – Request Your Complimentary Sample Now @ https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/71525/
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Scope and Methodology:
The market research report for Plastic for Consumer Electronics offers detailed insights into the key factors shaping industry growth, along with the challenges that may arise in the future. It equips stakeholders with a clear understanding of investment prospects, available product portfolios, and the competitive landscape within the Plastic for Consumer Electronics sector. The study also explores both quantitative and qualitative dimensions of the industry. As part of the MMR analysis, regional markets within the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market are examined extensively.
This report presents a comprehensive overview of all major and several minor market elements. The findings are based on data collected from both primary and secondary sources, including expert opinions, industry specialists, official websites, scientific journals, and company annual reports.
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Segmentation
by Product
•Polycarbonate (PC),
• Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
• Styrene-acrylonitrile resin (SAN)
• Acrylonitrile styrene acrylester (ASA)
• Polystyrene (PS)
• Poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA)
• Others
Feel free to request a complimentary sample copy or view a summary of the report @ https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/71525/
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Regional Insights
The market size, growth rate, import and export by region, and other relevant variables are all thoroughly analysed in this research. Understanding the Plastic for Consumer Electronics market conditions in different countries is feasible because to the researchs geographic examination. Africa, Latin America, the Middle East, Asia Pacific, and Europe put together make up the Plastic for Consumer Electronics market.
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Key Players
• Atotech (Germany)
• LG Chem Ltd. (South Korea)
• DowDuPont (United States)
• LyondellBasell (Netherlands)
• Trinseo(United States),
• INEOS Group (United Kingdom)
• SABIC (Saudi Arabia)
• ExxonMobil Corporation (United States)
Key questions answered in the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market are:
What is Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What is the growth rate of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Which are the factors expected to drive the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market growth?
What are the different segments of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What growth strategies are the players considering to increase their presence in Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What are the upcoming industry applications and trends for the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What are the recent industry trends that can be implemented to generate additional revenue streams for the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Who are the leading companies and what are their portfolios in Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What segments are covered in the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Explore More Market Reports:
Aluminum Foil Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-aluminum-foil-market/23912/
DevOps Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-devops-market/31505/
About Maximize Market Research:
Maximize Market Research is a multifaceted market research and consulting company with professionals from several industries. Some of the industries we cover include medical devices, pharmaceutical manufacturers, science and engineering, electronic components, industrial equipment, technology and communication, cars and automobiles, chemical products and substances, general merchandise, beverages, personal care, and automated systems. To mention a few, we provide market-verified industry estimations, technical trend analysis, crucial market research, strategic advice, competition analysis, production and demand analysis, and client impact studies.
Contact Maximize Market Research:
2nd Floor, Navale IT Park, Phase 3
Pune Banglore Highway, Narhe,
Pune, Maharashtra 411041, India
sales@maximizemarketresearch.com
+91 96071 95908, +91 9607365656
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Forecast, Regional Insights, and Competitive Landscape (2023-2029)
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Overview
Maximize Market Research is a Business Consultancy Firm that has published a detailed analysis of the “Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market”. The report includes key business insights, demand analysis, pricing analysis, and competitive landscape. The analysis in the report provides an in-depth aspect at the current status of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market, with forecasts outspreading to the year.
Gain Valuable Insights – Request Your Complimentary Sample Now @ https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/71525/
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Scope and Methodology:
The market research report for Plastic for Consumer Electronics offers detailed insights into the key factors shaping industry growth, along with the challenges that may arise in the future. It equips stakeholders with a clear understanding of investment prospects, available product portfolios, and the competitive landscape within the Plastic for Consumer Electronics sector. The study also explores both quantitative and qualitative dimensions of the industry. As part of the MMR analysis, regional markets within the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market are examined extensively.
This report presents a comprehensive overview of all major and several minor market elements. The findings are based on data collected from both primary and secondary sources, including expert opinions, industry specialists, official websites, scientific journals, and company annual reports.
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Segmentation
by Product
•Polycarbonate (PC),
• Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
• Styrene-acrylonitrile resin (SAN)
• Acrylonitrile styrene acrylester (ASA)
• Polystyrene (PS)
• Poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA)
• Others
Feel free to request a complimentary sample copy or view a summary of the report @ https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/71525/
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Regional Insights
The market size, growth rate, import and export by region, and other relevant variables are all thoroughly analysed in this research. Understanding the Plastic for Consumer Electronics market conditions in different countries is feasible because to the researchs geographic examination. Africa, Latin America, the Middle East, Asia Pacific, and Europe put together make up the Plastic for Consumer Electronics market.
Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market Key Players
• Atotech (Germany)
• LG Chem Ltd. (South Korea)
• DowDuPont (United States)
• LyondellBasell (Netherlands)
• Trinseo(United States),
• INEOS Group (United Kingdom)
• SABIC (Saudi Arabia)
• ExxonMobil Corporation (United States)
Key questions answered in the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market are:
What is Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What is the growth rate of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Which are the factors expected to drive the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market growth?
What are the different segments of the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What growth strategies are the players considering to increase their presence in Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What are the upcoming industry applications and trends for the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What are the recent industry trends that can be implemented to generate additional revenue streams for the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Who are the leading companies and what are their portfolios in Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
What segments are covered in the Plastic for Consumer Electronics Market?
Explore More Market Reports:
Aluminum Foil Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-aluminum-foil-market/23912/
DevOps Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-devops-market/31505/
About Maximize Market Research:
Maximize Market Research is a multifaceted market research and consulting company with professionals from several industries. Some of the industries we cover include medical devices, pharmaceutical manufacturers, science and engineering, electronic components, industrial equipment, technology and communication, cars and automobiles, chemical products and substances, general merchandise, beverages, personal care, and automated systems. To mention a few, we provide market-verified industry estimations, technical trend analysis, crucial market research, strategic advice, competition analysis, production and demand analysis, and client impact studies.
Contact Maximize Market Research:
2nd Floor, Navale IT Park, Phase 3
Pune Banglore Highway, Narhe,
Pune, Maharashtra 411041, India
sales@maximizemarketresearch.com
+91 96071 95908, +91 9607365656
·1K Lectures
·0 Avis